We have been utilizing the natural power of nature for millennia, even though renewable energy is frequently considered a solution for the future of our power demands. Windmills and water wheels powered granaries, and the fire was created by the sun for heat and light.
On the other hand, humans were increasingly reliant on fossil fuels such as coal and natural gas. The extensive use of various energy sources has been demonstrated to negatively influence the world, resulting in higher global temperatures, more extreme weather occurrences, and the destruction of natural ecosystems.
Recent breakthroughs in capture and storage and the worldwide push to achieve Greener Earth have increased renewable energy. So, what exactly is renewable energy? Let’s find out.
Renewable Energy Source
Renewable energy refers to endless and sustainable energy like the sun. It refers to energy sources that are less damaging to the environment than the most commonly utilized non-sustainable energy sources, such as coal. Alternative energy typically refers to both renewable and nonrenewable energy sources.
Types of Renewable Energy
Various renewable energy sources have been produced, each with benefits and drawbacks based on geographical location, use requirements, and even the time of year. The most common renewable energy sources are:
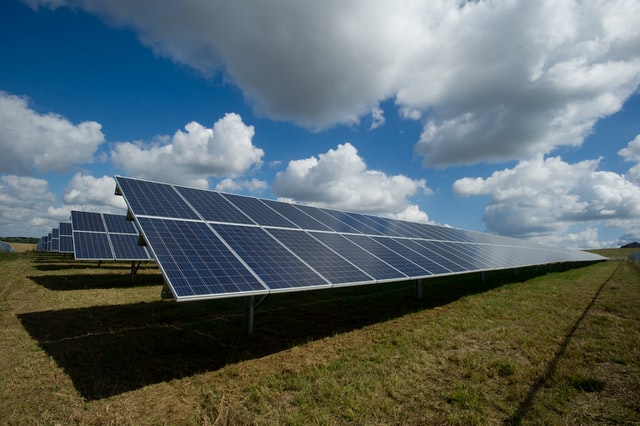
Solar Energy – One of our planet’s most plentiful and readily available energy sources is sunlight. The quantity of solar power that reaches earth in a single hour is sufficient to fulfill the planet’s whole annual energy requirements. Contact the Utility Bidder today to determine if this is the right energy type for you to switch to an eco-friendly lifestyle.
Wind Energy – Wind energy works similarly to old-fashioned windmills in that it uses the wind’s strength to turn a blade. The action of these blades used to force millstones to grind together to manufacture wheat, but now they power a generator that generates energy.
Hydro Energy – Hydropower is one of the most commercially established renewable energy sources. By creating a dam or barrier, a large reservoir may be used to regulate water in a way that drives a turbine and generates electricity.
Tidal Energy – Another type of hydro energy is tidal energy, which employs twice-daily tidal currents to power turbine turbines. Although tidal flow is not continuous, it is very predictable and can thus compensate for periods when the tide current is low, unlike some other hydro energy sources.
Geothermal Energy – The heat trapped in the Earth’s core is created by the steady decay of radioactive particles found in rocks; this is used for geothermal energy. We can send highly heated water to the surface via wells, which can be exploited as a hydrothermal resource to spin turbines and generate power.
Biomass Energy – This is turning plant-based solid fuel into energy. Although biomass is primarily a technique of burning organic materials to generate power, it is now a much cleaner and more energy-efficient process.
A Greener Future
As the world’s population expands, so does the demand for energy to power our homes, companies, and communities. To maintain a sustainable energy level and safeguard our world from climate change, we must innovate and expand renewable energy sources.
The number of renewable energy sources is likely to grow as the demand for electricity rises. This will lower the cost of renewable energy, which is good for the environment and good for our wallets.